
Key words: acetaminophen, paracetamol, N-acetyl- p-aminophenol (APAP), acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity, N-acetyl- p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI), glutathione, sulfation, liver transaminases, centrilobular hepatic necrosis, Rumack-Matthew nomogram, N-acetylcysteine (NAC)Īcetaminophen is the most commonly used analgesic–antipyretic medication given to children in the United States and worldwide. This article reviews the pathophysiology of acetaminophen metabolism, the clinical and diagnostic clues of an acute overdose, differential diagnoses, and management approaches including the use of the antidote, N-acetylcysteine (NAC), for acute acetaminophen overdose and toxicity in pediatric patients.
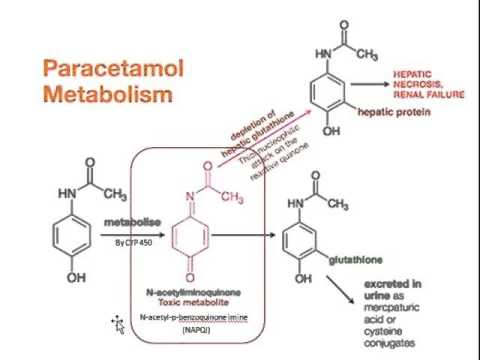
ABSTRACT: Acetaminophen is the most commonly used pain medication in the United States, and its ubiquity results in its being one of the most frequently implicated drugs in childhood poisonings.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
